The Verb To Have
Have is one of the most common verbs in the English language. It functions in various ways.
To have as a main verb
As a main verb “to have” implies the meaning of possession.
For example: “I have a job.” “I have a car.“ "I don't have any time."
In this form it does not take the continuous form (for that you have to use the auxiliary verb be).
For example: “I am having a shower.” “Are you having a good time?"
The forms of the verb “to have” are have and has for the present and had for the past.
As mentioned about "have" is often used to indicate possession (I have) or you might see (I have got).
Examples
To have as an auxiliary verb
The verb “to have” is used as an auxiliary verb to help other verbs create the perfect tense - auxiliary verb have [+ past participle].
For example, “I have studied English for five years;” or “I have never been to America.” "I have eaten."
For example:
The use of have to
In addition to the two forms, there is another use for have as a modal verb; have to or have got to. This, of course, must be followed by another verb "We have to do something".
To have something done
If something is done for you, in other words you haven't actually done it yourself, we use the structure "to have something done".
For example:-
"I have my hair cut once every six weeks." (I don't cut my own hair, my hairdresser cuts it for me.)
"My husband has the car serviced once a year." (He wouldn't have a clue how to service a modern car so, he takes it to the garage and they service it for us.)
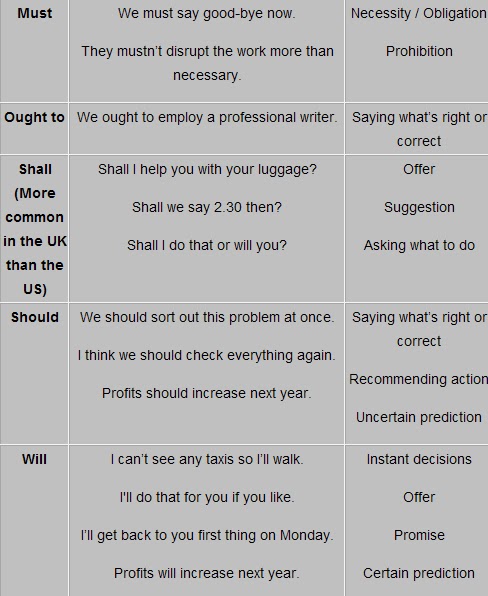
Modal Verbs
All the auxiliary verbs except be, do and have are called modals. Unlike other auxiliary verbs modals only exist in their helping form; they cannot act alone as the main verb in a sentence.
Be, do, and have also differ from the other auxiliaries in that they can also serve as ordinary verbs in a given sentence.
The modal verbs are:-
CAN / COULD / MAY / MIGHT / MUST / SHALL / SHOULD / OUGHT TO / WILL / WOULD
!Note The modal auxiliary verbs are always followed by the base form.
The verb used to, which is explained here, can also be used like a modal verb.
http://www.learnenglish.de/grammar/verbaux.htm
http://www.ego4u.com/en/cram-up/grammar/auxiliary-verbs